Sri Lanka Schools AL ICT Computer Networking (ICT Grade 12 Lesson 6 ). After studying this chapter, you will be able to understand the following:
- 6.1 Explores signals and their properties.
- 6.2 Explores signal transmission media.
- 6.3 Investigates how digital data is encoded using signal elements.
- 6.4 Explores the use of a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to connect two remote devices.
- 6.5 Investigates how the problem of connecting multiple devices into a network is addressed.
- 6.6 Explores the role of Media Access Control (MAC) protocol.
- 6.7 Explores how the multiple networks are interconnected to form the Internet.
- 6.8 Explores the role of transport protocols in the Internet.
- 6.9 Explores some applications on the Internet.
- 6.10 Investigates the role of reference models to describe the network architecture.
- 6.11 Investigates the security aspects of communication and protection of devices connected to the Internet.
- 6.12 Explores the role of ISPs and technologies used for connecting Home Networks to the Internet.
You can get better practical knowledge by watching the given videos related to the topics mentioned in the syllabus of this lesson AL ICT Computer Networking. By clicking on the relevant categories, you can see the description of the lesson related to the topic
? Learning Video Option 1 – Sinhala Medium – Play List Included 27 Videos with Question discussion
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - මං ද්වාරය | 05 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 07
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - මං ද්වාරය | 04 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 07
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - මං ද්වාරය | 03 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 07
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - මං ද්වාරය | 02 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 07
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - මං ද්වාරය | 01 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 07
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 10 වන පාඩම - TCP - IP නියමාවලි නිර්මිතය - 02 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 10
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 11 වන පාඩම - අන්තර්ජාලයට සම්බන්ධ කර ඇති උපාංගවලට ආරක්ෂණය සහ සන්නිවේදනයේ ඇති ආරක්ෂක ආකාර
-

06 වන ඒකකය | 11 වන පාඩම - අන්තර්ජාලයට සම්බන්ධ කර ඇති උපාංගවලට ආරක්ෂණය සහ සන්නිවේදනයේ ඇති ආරක්ෂක ආකාර
? Learning Video Option 2 – Sinhala Medium
Given below is an AL ICT resources Book prepared in relation to your syllabus.
For an enlarged view of the resources Book, ? Click Here
Related resources and links to this lesson
Resource Book Lesson Note Download Questions Syllabus
External Links
Online Network Diagram Tool https://cloud.smartdraw.com/?nsu=1
or https://app.creately.com/d/mcCPWIpZjj2/edit
AL ICT Computer Networking
Exploring the Foundation of Modern Connectivity
Are you curious about the intricate world of computer networking and how devices com
communicate with each other? In this article, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of AL ICT computer networking. From understanding signals and their properties to exploring the interconnection of multiple networks to form the Internet, we will embark on a journey to uncover the underlying principles that enable seamless connectivity in the digital age. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to explore the fascinating world of computer networking!
1. Introduction: The Power of Connectivity
In our modern world, connectivity plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Whether it’s sharing information, communicating with friends and family, or accessing vast amounts of knowledge, computer networks enable us to connect and collaborate like never before. AL ICT computer networking forms the backbone of this interconnected world, facilitating the seamless flow of data between devices. To better understand this intricate system, let’s delve into the core concepts that underpin computer networking.
2. Signals and Their Properties
Signals are the carriers of information in a network. Understanding their properties is essential to comprehend how data is transmitted and received. In this section, we will explore the different types of signals and their characteristics, including amplitude, frequency, and phase. By grasping these foundational concepts, we can gain insights into how data is encoded and transmitted across networks.
3. Signal Transmission Media
The transmission media act as the physical pathways for signals to travel from one device to another. This section will delve into various transmission media, such as guided media (e.g., twisted pair cables, fiber-optic cables) and wireless media (e.g., radio waves, microwaves). We will discuss their advantages, limitations, and applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of how signals traverse the network infrastructure.
4. Digital Data Encoding Using Signal Elements
In the digital realm, data needs to be encoded into signal elements for transmission. This section will explore different encoding techniques, such as amplitude shift keying (ASK), frequency shift keying (FSK), and phase shift keying (PSK). By examining these methods, we can comprehend how digital data is converted into signal elements, allowing for efficient transmission across networks.
5. Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) has been a vital communication infrastructure for connecting remote devices for decades. This section will shed light on the architecture and operation of PSTN, including concepts like local loops, trunk lines, and circuit-switched connections. By understanding the foundations of PSTN, we can appreciate the evolution of communication technologies.
6. Addressing the Problem of Connecting Multiple Devices
As networks grow and expand, connecting multiple devices becomes a challenge. This section will explore various techniques and protocols used to address this problem, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and network switches. By examining these solutions, we can comprehend how devices seamlessly integrate into a network, facilitating efficient communication and collaboration.
7. Media Access Control (MAC) Protocol
The Media Access Control (MAC) protocol plays a pivotal role in regulating access to the network medium. This section will delve into MAC protocols like CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) and CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance). Understanding these protocols is crucial for ensuring efficient and fair utilization of network resources.
8. Interconnecting Networks to Form the Internet
The Internet has revolutionized the way we connect and share information globally. In this section, we will explore the interconnection of multiple networks to form the Internet. Concepts like routers, IP addressing, and routing protocols will be discussed, offering insights into the infrastructure that powers the world wide web.
9. The Role of Transport Protocols in the Internet
Transport protocols, such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), ensure reliable and efficient data delivery across the Internet. This section will explain the functionalities of these protocols, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and typical use cases. By understanding transport protocols, we can appreciate the robustness of data transmission on the Internet.
10. Applications on the Internet
The Internet hosts a vast array of applications that enrich our digital experiences. This section will explore popular Internet applications such as email, web browsing, file transfer, and video streaming. By uncovering the functionalities and underlying technologies of these applications, we can better grasp the diverse possibilities offered by the Internet.
11. Reference Models and Network Architecture
To describe network architecture, reference models play a vital role. This section will investigate prominent models like the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model and the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) model. By examining these models, we can establish a comprehensive framework for understanding the organization and functionality of computer networks.
12. Security Aspects of Communication and Device Protection
In an interconnected world, ensuring the security of communication and protecting devices is paramount. This section will explore the security aspects of computer networking, including encryption, firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection systems. By understanding these security measures, we can appreciate the efforts made to safeguard data and devices in the digital realm.
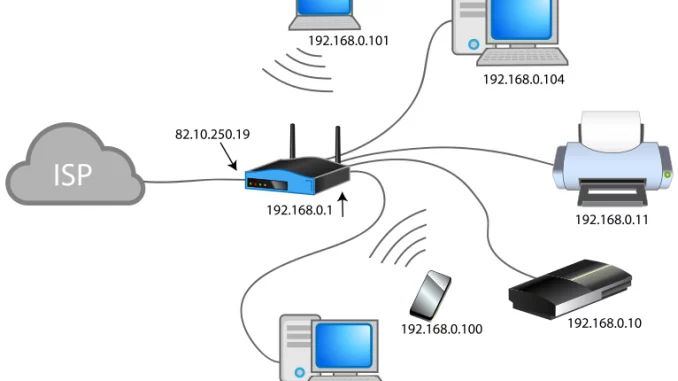
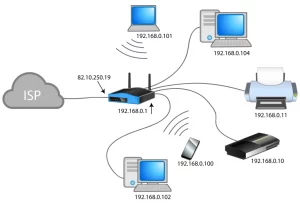
13. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Home Network Connectivity
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) play a crucial role in connecting home networks to the Internet. This section will delve into the technologies used by ISPs, such as DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), cable internet, and fiber-optic internet. By understanding the infrastructure provided by ISPs, we can gain insights into how our homes are connected to the vast network of networks.
14. Conclusion
In conclusion, AL ICT computer networking forms the foundation of modern connectivity. By exploring the various aspects of computer networking, from signals and transmission media to interconnecting networks and security measures, we have gained a comprehensive understanding of how devices communicate in the digital realm. The power of networking extends far beyond our screens, shaping the way we live, work, and connect with the world.
FAQs
- Q: What are the essential properties of signals in a computer network? A: Signals in a computer network possess properties such as amplitude, frequency, and phase.
- Q: How are multiple devices connected to a network? A: Multiple devices are connected to a network using techniques like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and network switches.
- Q: What is the role of MAC protocol in computer networking? A: The MAC protocol regulates access to the network medium, ensuring fair utilization of network resources.
- Q: How are multiple devices interconnected to form the Internet? A: Multiple devices are interconnected to form the Internet through routers, IP addressing, and routing protocols.
- Q: What are some common Internet applications? A: Common Internet applications include email, web browsing, file transfer, and video streaming.
- Q: What are some security measures in computer networking? A: Security measures in computer networking include encryption, firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection systems.


















Leave a Reply