Sri Lanka Schools AL ICT Information Systems (ICT Grade 12 Lesson 7 ). After studying this chapter, you will be able to understand the following:
- 7.1 Explores the characteristics of systems.
- 7.2 Compares and contrasts different types of manmade systems in terms of their objectives and functionality.
- 7.3 Explores different information system development models and methods.
- 7.4 Examines the Structured System Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM).
- 7.5 Investigates the need for a new information system and its feasibility.
- 7.6 Uses different methods to analyze the current system.
- 7.7 Designs the proposed system.
- 7.8 Develops and test the proposed system.
- 7.9 Deploys the developed system.
- 7.10 Describes system implementation with off-the-shelf packaged systems.
You can get better practical knowledge by watching the given videos related to the topics mentioned in the syllabus of this lesson AL ICT Information Systems. By clicking on the relevant categories, you can see the description of the lesson related to the topic
? Learning Video Option 1 – Sinhala Medium – Play List Included 16 Videos with Question discussion
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 10 වන පාඩම - පෙර නිමි පැකේජ පද්ධති සමඟ නව පද්ධති ක්රියාත්මක කිරීම - 01 වන කොටස
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 09 වන පාඩම - යෝජිත පද්ධතිය ක්රියාත්මක කිරීම - 1 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 06 Lesson 10
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 08 වන පාඩම - යෝජිත පද්ධතිය සංවර්ධනය - 02 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 07 Lesson 08
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 08 වන පාඩම - යෝජිත පද්ධතිය සංවර්ධනය - 01 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 07 Lesson 08
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 07 වන පාඩම - යෝජිත පද්ධතිය සැලසුම් කිරීම - 01 වන කොටස | AL IT Unit 07 Lesson 7
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 06 වන පාඩම - පවතින පද්ධතිය විශ්ලේෂණය කිරීම සඳහා වෙනස් විධික්රම භාවිතය - 03 වන කොටස
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 06 වන පාඩම - පවතින පද්ධතිය විශ්ලේෂණය කිරීම සඳහා වෙනස් විධික්රම භාවිතය - 02 වන කොටස
-

07 වන ඒකකය | 06 වන පාඩම - පවතින පද්ධතිය විශ්ලේෂණය කිරීම සඳහා වෙනස් විධික්රම භාවිතය - 01 වන කොටස
-

A/L ICT (තොරතුරු පද්ධති සිංහලෙන්) Information Systems in sinhala - part 7.1& 7.2 (IS)
-

A/L ICT(තොරතුරු පද්ධති සිංහලෙන්) Information Systems in sinhala - part 7.3(System Develoment models)
-

A/L ICT (පද්ධති සිංහලෙන්) Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.4 & 7.5(SSADM හා පද්ධති හඳුනාගැනීම)
-

A/L ICT (පද්ධති සිංහලෙන්) Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.6 - I (පද්ධති විශ්ලේෂණය හා BAM)
-

A/L ICT (DFD සිංහලෙන්) Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.6 - II (දත්ත ගැලීම් සටහන් / DFD)
-

A/L ICT Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.6 - III (ලේඛන ගැලීම් සටහන් & BSO)
-

A/L ICT Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.7 (තාර්කික සැලසුම් මෙවලම්)
-

A/L ICT Information Systems in sinhala- part 7.8 (පද්ධති සංවර්ධනය හා පරීක්ෂාව)
Given below is an AL ICT resources Book prepared in relation to your syllabus.
For an enlarged view of the resources Book, ? Click Here
Related resources and links to this lesson
External Links
Software Design Diagram Tools https://cloud.smartdraw.com/?nsu=1
AL ICT Information Systems: Exploring Characteristics and Development
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, information systems play a crucial role in various industries and sectors. AL ICT (Applied Learning Information and Communication Technology) provides a comprehensive understanding of information systems and their development processes. This article will delve into the key aspects of AL ICT Information Systems, exploring their characteristics, comparing different types of systems, examining development models and methods, and discussing the importance of system analysis and design. Additionally, we will explore the feasibility of new information systems, analyze existing systems, design proposed systems, and discuss implementation and deployment. Let’s embark on this journey of understanding the world of AL ICT Information Systems.
1. Characteristics of Systems
When exploring AL ICT Information Systems, it is essential to understand their fundamental characteristics. These characteristics define the nature and behavior of these systems. Some key characteristics include:
1.1 Integration
AL ICT Information Systems are designed to integrate various components, processes, and data sources to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. The integration allows different parts of the system to work together seamlessly.
1.2 Interconnectivity
AL ICT Information Systems facilitate communication and data exchange between different entities within the system and with external systems. Interconnectivity enables the sharing of information and resources, promoting collaboration and effective decision-making.
1.3 Scalability
Information systems need to be scalable to accommodate growth and changing requirements. Scalability ensures that the system can handle increased workloads, data volumes, and user interactions without compromising performance.
1.4 Flexibility
AL ICT Information Systems should be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business needs and technological advancements. Flexibility allows for modifications and updates to the system without significant disruptions, enabling organizations to stay agile and responsive.
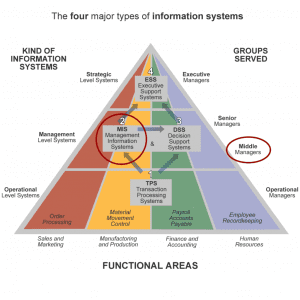
2. Types of Manmade Systems
In AL ICT, it is important to understand the different types of manmade systems and their objectives and functionality. Let’s explore some of the common types:
2.1 Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
TPS is designed to process and record routine transactions, such as sales, purchases, and inventory management. They ensure accurate and efficient handling of day-to-day operational data.
2.2 Management Information Systems (MIS)
MIS provides managers with timely and relevant information to support decision-making and strategic planning. These systems gather data from various sources, process it, and present it in a format suitable for analysis and decision-making.
2.3 Decision Support Systems (DSS)
DSS assists decision-makers by providing them with interactive tools and models to analyze data and evaluate different scenarios. These systems help in complex decision-making processes, offering insights and recommendations.
2.4 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems integrate various business processes and functions, including finance, human resources, inventory management, and customer relationship management. They provide a centralized platform for seamless information flow and collaboration across departments.
3. Information System Development Models and Methods
AL ICT covers different models and methods used in the development of information systems. These frameworks guide the systematic and structured approach to designing and implementing robust systems. Some commonly used models and methods include:
3.1 Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model follows a sequential approach, with distinct phases such as requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and deployment. Each phase is completed before moving on to the next, ensuring a well-defined and linear development process.
3.2 Agile Methodology
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize iterative and collaborative development. They prioritize flexibility, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Agile teams work in short cycles called sprints to deliver increments of the system and gather feedback from stakeholders.
3.3 Rapid Application Development (RAD)
RAD focuses on accelerated development through the use of prototyping and iterative feedback. It aims to reduce the time-to-market by involving users early in the development process and incorporating their feedback into subsequent iterations.
3.4 Object-Oriented Analysis and Design (OOAD)
OOAD emphasizes the modular design of systems by representing real-world entities as objects with properties and behaviors. This approach promotes code reusability, maintainability, and scalability.
4. Structured System Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM)
SSADM is a widely used approach in AL ICT for analyzing and designing information systems. It follows a phased approach, encompassing stages such as feasibility study, requirements analysis, logical design, physical design, and implementation. SSADM ensures a thorough understanding of the system requirements and a well-structured design process.
5. Need for a New Information System and Feasibility
Organizations often find the need to develop new information systems to address evolving business requirements or technological advancements. Before embarking on the development process, a feasibility study is conducted to assess the viability and potential success of the proposed system. The study examines various aspects, including technical feasibility, economic viability, legal and regulatory compliance, and operational considerations.
6. Analysis of the Current System
Before designing a new information system, it is crucial to analyze the existing system to identify its strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Various methods can be employed, such as interviews, surveys, data analysis, and observations. Through careful analysis, organizations gain insights into the current system’s functionality, limitations, and user requirements.
7. Designing the Proposed System
Based on the analysis and requirements gathering, the next step is designing the proposed system. This involves creating a blueprint that outlines the system’s structure, components, interfaces, and functionality. Design techniques such as flowcharts, data flow diagrams, and entity-relationship diagrams are employed to visually represent the system’s design.
8. Developing and Testing the Proposed System
With the design in place, the development phase begins. Programmers and developers code the system, bringing it to life. It is crucial to follow coding standards, best practices, and quality assurance processes during development. Thorough testing is conducted to identify and rectify any issues, ensuring the system meets the specified requirements.
9. Deployment of the Developed System
Once the development and testing phases are complete, the system is ready for deployment. It is crucial to carefully plan and execute the deployment process, considering factors such as user training, data migration, system configuration, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. A smooth deployment ensures minimal disruption to the organization’s operations.
10. System Implementation with Off-the-Shelf Packaged Systems
In some cases, organizations opt for off-the-shelf packaged systems instead of developing custom solutions. These systems provide pre-built functionalities that can be configured to meet specific requirements. Implementation of packaged systems involves selecting the appropriate software, customization, integration with existing systems, and user training.
Conclusion
AL ICT Information Systems are the backbone of modern organizations, enabling efficient operations, informed decision-making, and strategic planning. Understanding the characteristics of systems, different types of manmade systems, development models and methods, and the analysis, design, and deployment processes are crucial for aspiring ICT professionals. By following structured approaches like SSADM, organizations can ensure the successful development and implementation of robust information systems that drive business growth and innovation.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the key characteristics of AL ICT Information Systems?
AL ICT Information System has several key characteristics, including integration, interconnectivity, scalability, and flexibility. These characteristics enable seamless operations, data exchange, adaptability, and growth within organizations.
2. What are the different types of manmade systems in AL ICT?
In AL ICT, there are various types of manmade systems, such as Transaction Processing Systems (TPS), Management Information Systems (MIS), Decision Support Systems (DSS), and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems. Each type serves different objectives and functionalities within an organization.
3. Which development models and methods are commonly used in AL ICT?
AL ICT utilizes different development models and methods, including the Waterfall Model, Agile Methodology, Rapid Application Development (RAD), and Object-Oriented Analysis and Design (OOAD). These frameworks provide structured approaches to system development, emphasizing sequential or iterative processes, adaptability, and modularity.
4. What is SSADM, and how does it contribute to AL ICT?
SSADM, or Structured System Analysis and Design Methodology, is a widely used approach in AL ICT for analyzing and designing information systems. It follows a phased approach, ensuring a thorough understanding of system requirements and a structured design process. SSADM enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of system development.
5. Why is a feasibility study important in information system development?
A feasibility study is crucial in information system development as it assesses the viability and potential success of the proposed system. It examines technical feasibility, economic viability, legal and regulatory compliance, and operational considerations. A feasibility study helps organizations make informed decisions and mitigate risks before investing resources into system development.






















Leave a Reply