Introduction: In recent years, the skies have seen a new constellation of satellites streaking across the horizon – Starlink. This ambitious project, spearheaded by SpaceX and its visionary CEO Elon Musk, aims to revolutionize internet connectivity across the globe. But how does Starlink work, and what sets it apart from traditional internet providers? Let’s delve into the intricacies of this groundbreaking system.
Understanding Starlink: Starlink is essentially a satellite internet constellation comprising thousands of small satellites orbiting the Earth. Unlike traditional internet infrastructure that relies on ground-based networks of cables and towers, Starlink beams internet connectivity directly from space to user terminals on the ground.
Key Components of Starlink:
- Satellite Constellation: Starlink’s backbone consists of a vast network of small satellites, each weighing around 260 kilograms. These satellites orbit the Earth at altitudes ranging from 340 to 1,200 kilometers, forming a dense mesh network that covers most of the planet’s surface.
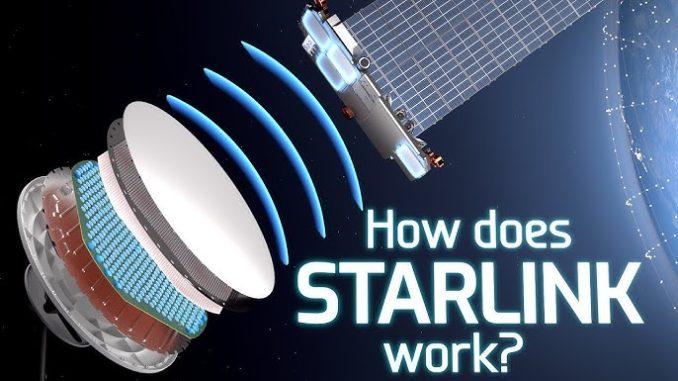
- User Terminals: At the heart of Starlink’s user experience are the user terminals, also known as phased-array antennas. These compact, pizza-box-sized devices are installed at the user’s location – be it a home, business, or remote area. The terminals communicate with the satellites overhead, establishing a high-speed internet connection.
- Ground Stations: Ground stations serve as the link between the Starlink satellites and the broader internet infrastructure. They receive data from the satellites and relay it to terrestrial networks, ensuring seamless connectivity for users.
How Starlink Works:
- Satellite Communication: When a user initiates an internet request, the user terminal communicates with nearby Starlink satellites. These satellites form a relay chain, transmitting the data from one satellite to another until it reaches a satellite directly overhead a ground station.
- Ground Station Relay: Once the data reaches a satellite directly above a ground station, it’s beamed down to the station via radio waves. From there, the data is transferred to the internet backbone, typically through fiber-optic cables, for routing to its final destination.
- Low Earth Orbit Advantage: Unlike traditional geostationary satellites that orbit at higher altitudes, Starlink satellites operate in low Earth orbit (LEO). This proximity reduces signal latency, delivering faster response times compared to conventional satellite internet services.
Benefits of Starlink:
- Global Coverage: Starlink’s satellite constellation offers internet access to remote and underserved regions where traditional infrastructure is impractical or unavailable.
- High-Speed Connectivity: With download speeds ranging from 50 to 150 megabits per second (Mbps) and low latency, Starlink provides competitive performance, rivaling many terrestrial broadband services.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Starlink’s modular design allows for rapid deployment and scalability, making it well-suited for addressing evolving connectivity needs, including disaster recovery and emergency response efforts.
Conclusion: Starlink represents a paradigm shift in internet connectivity, leveraging space-based infrastructure to deliver high-speed, low-latency internet access to virtually any location on Earth. As SpaceX continues to expand its satellite constellation and refine its technology, Starlink promises to bridge the digital divide and unlock new opportunities for communities worldwide. With its innovative approach and ambitious vision, Starlink is poised to reshape the future of internet connectivity.
More Detail https://www.starlink.com/


Leave a Reply