What are the three main stages of the data lifecycle?
How is data distinguished from information?
What are three characteristics of valuable information?
What is meant by “big data” in ICT?
What is one drawback of manual data processing methods?
Answers and Descriptions:
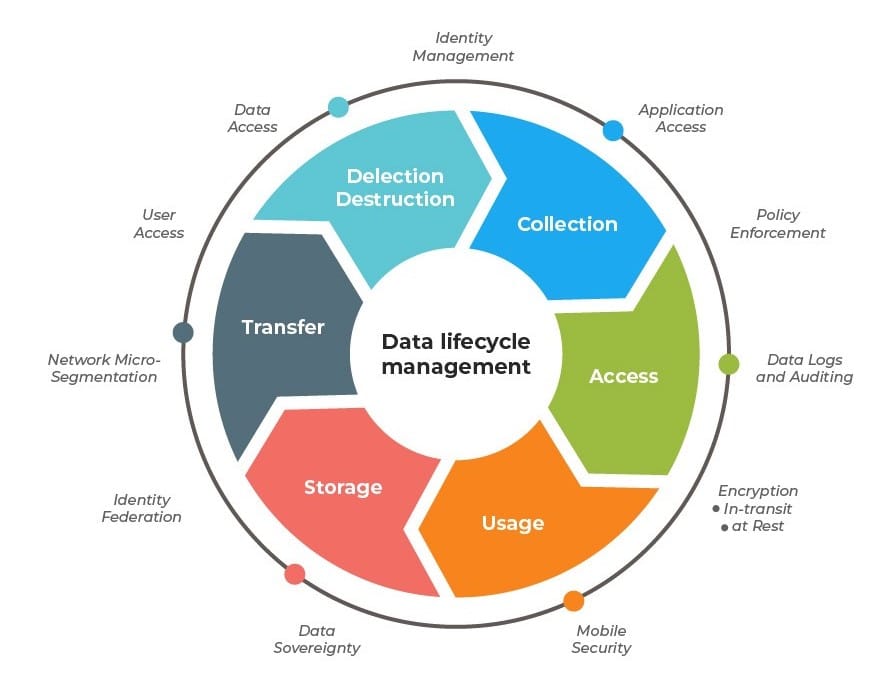
Answer: Creation, management, and removal of obsolete data.
Description: The data lifecycle outlines how data is handled from its inception to its eventual disposal. Creation involves generating or collecting data, management includes organizing and maintaining it, and removal ensures obsolete data is securely deleted to free up resources and maintain privacy. Understanding this cycle helps students appreciate the structured approach to handling data in ICT systems.
Image:
Answer: Data is raw, unprocessed facts, while information is processed data that has meaning and context.
Description: Data, such as numbers or symbols, lacks meaning until it is processed (e.g., analyzed or organized) to become information, which is useful for decision-making. For example, “25” is data, but “25°C is the room temperature” is information. This distinction is critical for understanding how ICT systems transform data into actionable insights.Answer: Timeliness, accuracy, and presented within context.
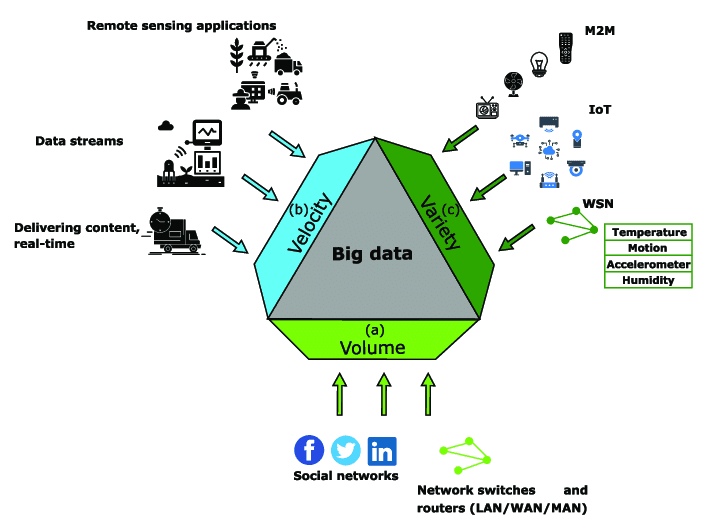
Description: Valuable information must be timely (available when needed), accurate (free from errors), and contextual (relevant to the situation). These characteristics ensure information supports effective decision-making, reducing uncertainty and enhancing understandability, which is vital in today’s fast-paced knowledge society.Answer: Big data refers to large, complex datasets that require advanced tools for processing and analysis.
Description: Big data involves high volume, velocity, and variety of data, such as social media posts or sensor data. Recognizing its needs (e.g., storage, analytics) helps students understand how ICT handles modern data challenges, enabling applications like predictive modeling in business or healthcare.
Image:
Answer: Inconsistency and duplication in data.
Description: Manual methods, such as paper-based records, often lead to inconsistent or duplicated data due to human errors or lack of synchronization. This drawback highlights the need for ICT to ensure data integrity and efficiency, a key concept for students to grasp when studying technology’s role in data management.