Question Title: Fundamentals of Database Concepts
- What is a database, and what are its main advantages?
- Name three key features of a relational database and explain one in detail.
- What are the key elements to consider when creating a manual database table?
- Why is it important to define data types when converting a manual database to an electronic one?
- What is the difference between a primary key and a foreign key in a relational database?
Ruwan Suraweera Changed status to publish 6 days ago
Answers and Descriptions:
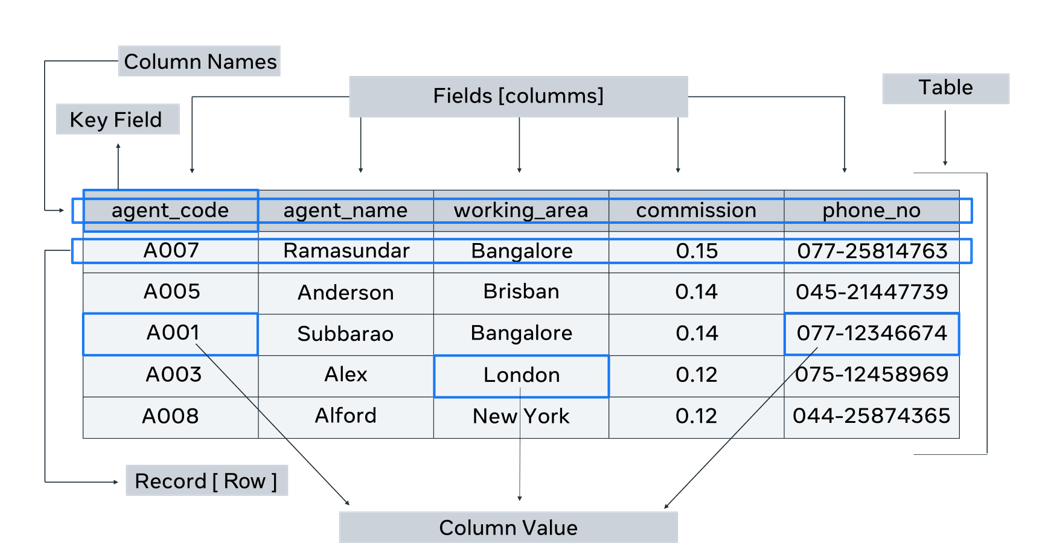
- Answer: A database is an organized collection of data, typically stored and accessed electronically. Its main advantages include efficient data management, reduced redundancy, improved accuracy, and enhanced security.
Description: A database helps store and retrieve information systematically. For example, a school database can store student records without duplicating data (redundancy), ensuring accuracy and security for sensitive information. - Answer: Three key features are absence of redundancy, consistency, and integrity. Consistency ensures that data remains uniform across the database (e.g., a student’s name is spelled the same everywhere).
Description: These features make databases reliable. Consistency prevents confusion, like having “John Doe” in one record and “Jon Doe” in another, which could happen in manual systems. - Answer: Key elements include field name (e.g., “Student ID”), unique field (e.g., a primary key), data types (e.g., text, number), and field size (e.g., maximum characters).
Description: These elements ensure the table is structured. For instance, “Student ID” as a unique field prevents duplicate entries, while data types define what kind of data can be entered. - Answer: Data types (e.g., text, number) ensure the electronic database processes and stores data correctly, matching the manual design.
Description: For example, if “Age” is a number in the manual database, setting it as a number type in software allows calculations like averaging ages, which wouldn’t work if set as text. - Answer: A primary key uniquely identifies each record in a table (e.g., “Student ID”), while a foreign key links to a primary key in another table (e.g., “Student ID” in a “Grades” table).
Description: This relationship connects tables. For instance, a “Students” table has “Student ID” as the primary key, and a “Grades” table uses it as a foreign key to associate grades with students.
Ruwan Suraweera Changed status to publish May 22, 2025
