Question Title: Library Database System Basics
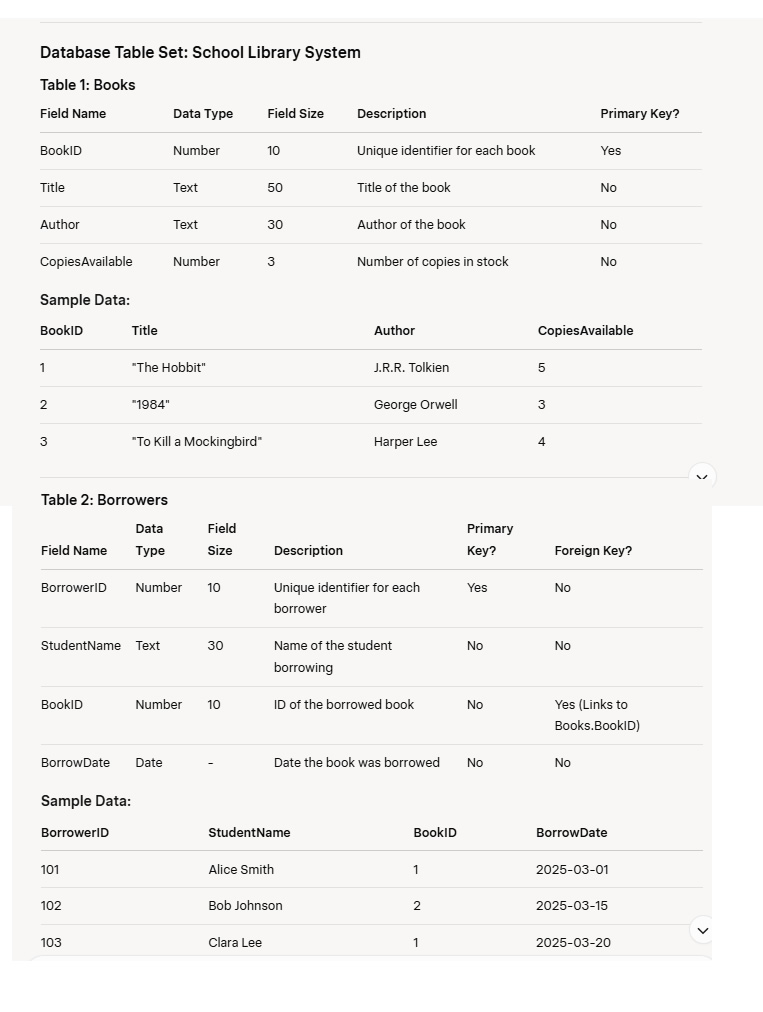
- What is the main purpose of the “School Library System” database shown above?
- Why was “BookID” chosen as the primary key in the “Books” table?
- Why is “CopiesAvailable” set as a Number data type instead of Text in the “Books” table?
- How does the “BookID” field connect the “Books” and “Borrowers” tables?
- How would you set up the relationship between “Books” and “Borrowers” in a DBMS like Microsoft Access?
Question Title: Advanced Library Database Operations
- Based on the sample data, which book has been borrowed more than once, and how can the database confirm this?
- What would happen in the DBMS if you tried to add a record to “Borrowers” with a BookID that doesn’t exist in “Books” (e.g., BookID 4)?
Ruwan Suraweera Changed status to publish May 23, 2025
Answers and Descriptions:
- Answer: The main purpose is to track books and their borrowers, ensuring efficient management of library resources.
Description: This database helps librarians know which books are available, who has borrowed them, and when, reducing manual tracking errors and improving efficiency. - Answer: “BookID” is unique for each book, ensuring no two books have the same identifier, which prevents duplication.
Description: A primary key like “BookID” (e.g., 1, 2, 3) uniquely identifies each record. Titles or authors could repeat (e.g., multiple books by Tolkien), but “BookID” cannot. - Answer: “CopiesAvailable” is a numeric value (e.g., 5, 3) that may need calculations (e.g., subtracting when borrowed), which requires a Number data type.
Description: If it were Text, you couldn’t perform math operations like reducing stock when a book is borrowed. Number ensures functionality in an electronic system. - Answer: “BookID” is the primary key in “Books” and a foreign key in “Borrowers,” linking each borrowed book to its details in the “Books” table.
Description: For example, BorrowerID 101 (Alice) has BookID 1, which matches “The Hobbit” in the “Books” table, showing what she borrowed. - Answer: In the DBMS, drag “BookID” from the “Books” table to “BookID” in the “Borrowers” table in the Relationships window to create a one-to-many link.
Description: One book (e.g., BookID 1) can be borrowed by many students (e.g., Alice and Clara), and the DBMS enforces this link to maintain data integrity.
Question Title: Advanced Library Database Operations
Answers and Descriptions:
- Answer: “The Hobbit” (BookID 1) has been borrowed twice (by Alice and Clara), confirmed by checking the “BookID” in the “Borrowers” table.
Description: The relational link shows BookID 1 appears in two records (BorrowerID 101 and 103), proving its popularity without needing manual counts. - Answer: The DBMS would reject the record or show an error because the foreign key “BookID” must match an existing primary key in “Books” to maintain referential integrity.
Description: If BookID 4 isn’t in “Books,” adding it to “Borrowers” would break the relationship (e.g., no book details exist), so the system prevents this.
Ruwan Suraweera Changed status to publish May 22, 2025
