Use the interactive tools below to apply concepts from **Competency 7: Systems Analysis and Design** of the ICT syllabus.
📝 Instructions & Competency Aims
How to Use
Click any button in the navigation bar below to switch to the corresponding tool. Only one tool is active at a time.
- **DFD Canvas:** Click the shape button, then click on the canvas to place it. Click **Data Flow (Arrow)**, then click twice (start/end) to draw a flow. To **Delete**, click on a shape/arrow once to select it, then click **Delete Selected**.
- **Comparator/Explorer:** Click the cards/tabs to view details.
- **Deployment/Package:** Select options and click 'Analyze' to receive feedback.
Competency 7 Aims Breakdown
| Tool | Syllabus Competency | Aim |
|---|---|---|
| Classifier | 7.1 | Recalls the definition and characteristics of systems. |
| Comparator | 7.2 | Compares objectives and functionality of IS types (TPS, MIS, DSS, ESS, KMS, ERP). |
| SDLC Explorer | 7.3 | Lists and briefly describes system development models and methodologies. |
| Feasibility | 7.5 | Describes the need for feasibility study and lists its types (Technical, Economic, Operational, Organizational). |
| Requirement Analyzer | 7.6 | Describes types of requirements (Functional vs. Non-functional). |
| DFD Canvas | 7.6/7.7 | Draws DFDs and writes Elementary Process Descriptions (EPD). |
| Deployment Selector | 7.9 | Describes the methods of deployment (Parallel, Direct, Pilot, Phased). |
| Package Analyzer | 7.10 | Describes the costs/benefits of off-the-shelf packages and performs process gap analysis. |
System Classification Tool (Comp 7.1)
Aim: Recalls the definition and characteristics of systems.
Enter a system name to see how it's classified (Open/Closed, Natural/Manmade, Living/Physical).
Information System Type Comparator (Comp 7.2)
Aim: Compares and contrasts different types of manmade systems in terms of their objectives and functionality.
TPS
Objective: Process high-volume, routine transactions.
Users: Operational staff, clerks.
Example: Point-of-Sale (POS) system, ATM.
MIS
Objective: Provide structured reports for middle management.
Users: Middle managers, department heads.
Example: Sales performance reports.
DSS
Objective: Support non-routine decision making using models.
Users: Senior managers, analysts.
Example: Supply chain optimization tool.
ESS
Objective: Facilitate strategic, unstructured decision making for top executives.
Users: Executive Management.
Example: Dashboard displaying organizational KPIs.
KMS
Objective: Capture, store, and distribute knowledge and expertise.
Users: Experts, organizational staff.
Example: Internal wiki, Best Practices Database.
ERP
Objective: Integrate all data and processes across the organization.
Users: All departments (Finance, HR, Supply Chain).
Example: SAP, Oracle ERP Cloud.
Requirement Analyzer: Functional vs. Non-functional (Comp 7.6)
Aim: Describes type of requirements with examples for a given system.
Functional requirements describe **what the system must do**. Non-functional requirements describe **how well** the system must perform (quality attributes).
SDLC Model Explorer (Comp 7.3)
Aim: Lists and briefly describes system development models and investigates their applicability.
Waterfall Model - Sequential Flow
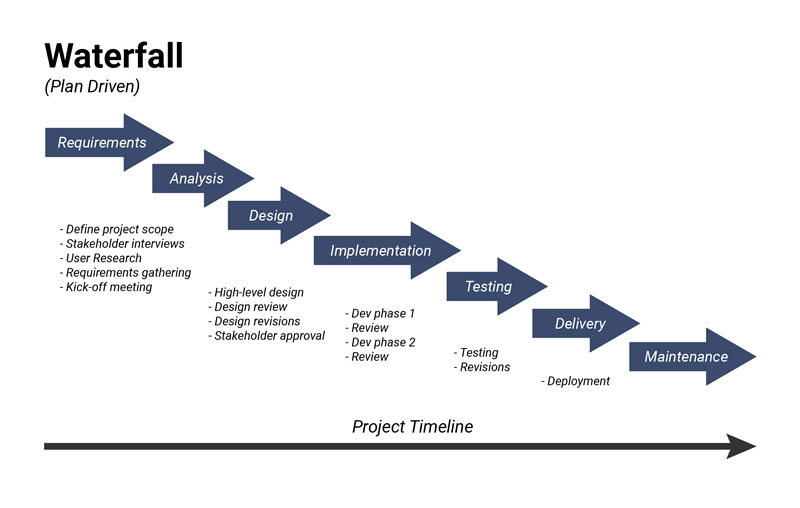
Phases: Project Planning → Requirements → Analysis → Design → Coding → Testing → Deployment.
Characteristics: Sequential, document-driven, each phase must be fully completed before the next begins.
Applicability: Best for projects with well-defined, stable requirements.
Spiral Model
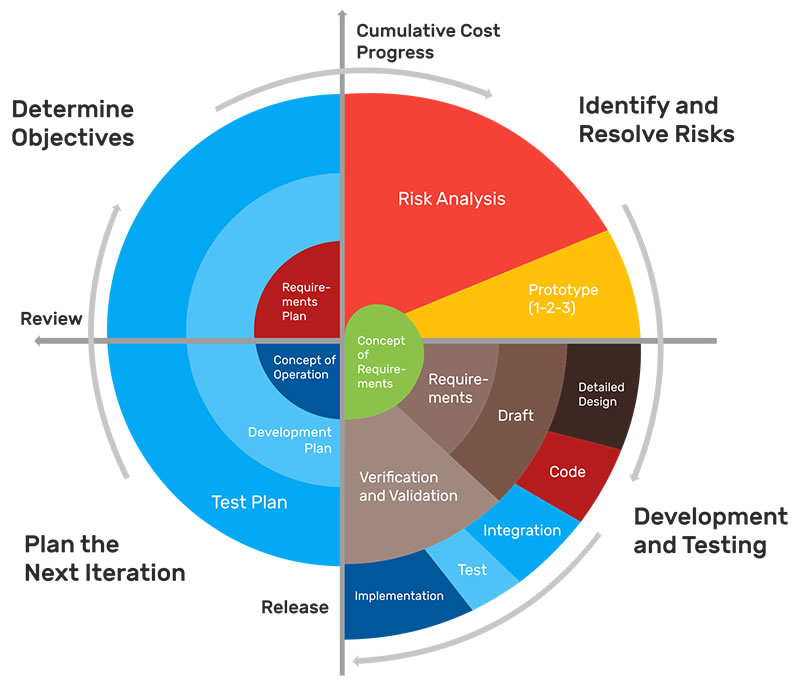
Phases: Repeated cycles of (Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, Evaluation).
Applicability: Best for large, complex, and high-risk projects. Risk reduction is key.
Agile Model

Phases: Iterative cycles (Sprints) with continuous feedback and delivery.
Applicability: Best for projects with rapidly changing requirements, emphasizing customer collaboration.
Prototyping / Rapid Application Development (RAD)
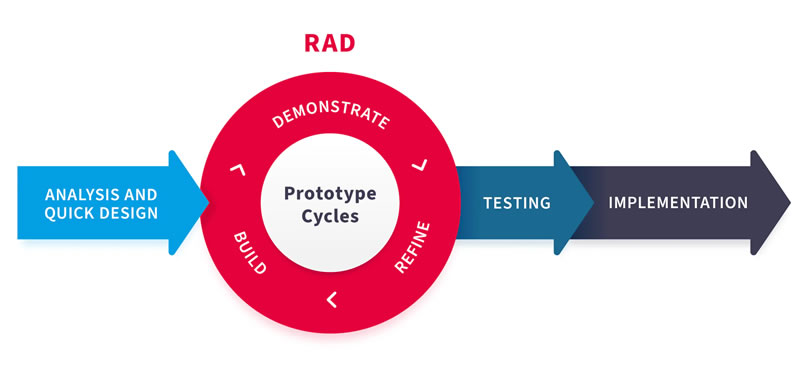
Phases: Quick building of a working system (prototype) for user feedback, followed by iteration or abandonment.
Applicability: Useful when requirements are unclear or immediate user validation is critical.
Methodology Note (Comp 7.3)
The two main methodologies are Structured and **Object-Oriented**.
SDLC Event/Activity Analyzer (Comp 7.3)
Aim: Relate a development activity to the most suitable SDLC model and its phase.
Select an activity to see which model is most appropriate.
Feasibility Study Analyzer (Comp 7.5)
Aim: Describes the need for feasibility study and lists its types.
Analyze the four types of feasibility using the checklist below. Note any **showstoppers** (fatal issues).
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) Canvas (Comp 7.6/7.7)
Aim: Draws Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) and writes Elementary Process Descriptions (EPD).
Design your DFD. Remember a full analysis includes a Context Diagram (Level 0) and breaking down processes into Elementary Process Descriptions (EPD).
Instructions: Click a **Shape** button, then click on the canvas to place it. Click **Data Flow (Arrow)**, then click twice on the canvas (start/end) to draw a flow. To **Delete**, click on a shape/arrow once to select it (it will get a border), then click **Delete Selected**.
DFD Symbols Legend:
System Deployment Strategy Selector (Comp 7.9)
Aim: Describes the methods of deployment of the developed system.
Scenario 1: "Greenwich Bank" Core Banking System
The bank is replacing its old core banking system. The new system is critical, and any downtime or data loss would be catastrophic. *Hint: Prioritize safety.*
Scenario 2: "Metro University" Student Portal
The university is implementing a new student portal across all departments. Some departments are resistant to change. *Hint: Use a small test group/department first.*
Scenario 3: "QuickMart Retail Chain" Inventory System
A retail chain with 50 stores nationwide is rolling out a new inventory management system. *Hint: Implement site-by-site or geographically.*
Scenario 4: "TechStart Inc." CRM System
A small startup with 15 employees is implementing a CRM system. They have limited IT staff and budget, but need the system operational quickly to support sales growth. *Hint: Minimize cost/duration.*
Scenario 5: "City General" Electronic Health Records (EHR)
The hospital is replacing the entire EHR system. Due to high regulation, complexity, and life-critical operations, risk must be zero. *Hint: Absolute minimum risk.*
Scenario 6: National Tax Filing System Update
The government is rolling out a major update to its tax filing system. The scope is massive (millions of users), but the changes are modular (e.g., new form processing, new payment system). *Hint: Gradual, manageable segments.*
Off-the-Shelf Package Analyzer (Comp 7.10)
Aim: Describes the costs and benefits of off-the-shelf packages and identifies process gap analysis.
Analyze COTS (Commercial Off-the-Shelf) implementation by focusing on the **Business Process Gap Analysis**.
Scenario: Your company needs a new accounting system. You're evaluating a popular off-the-shelf package that handles most functions but doesn't support your unique commission calculation method.
